
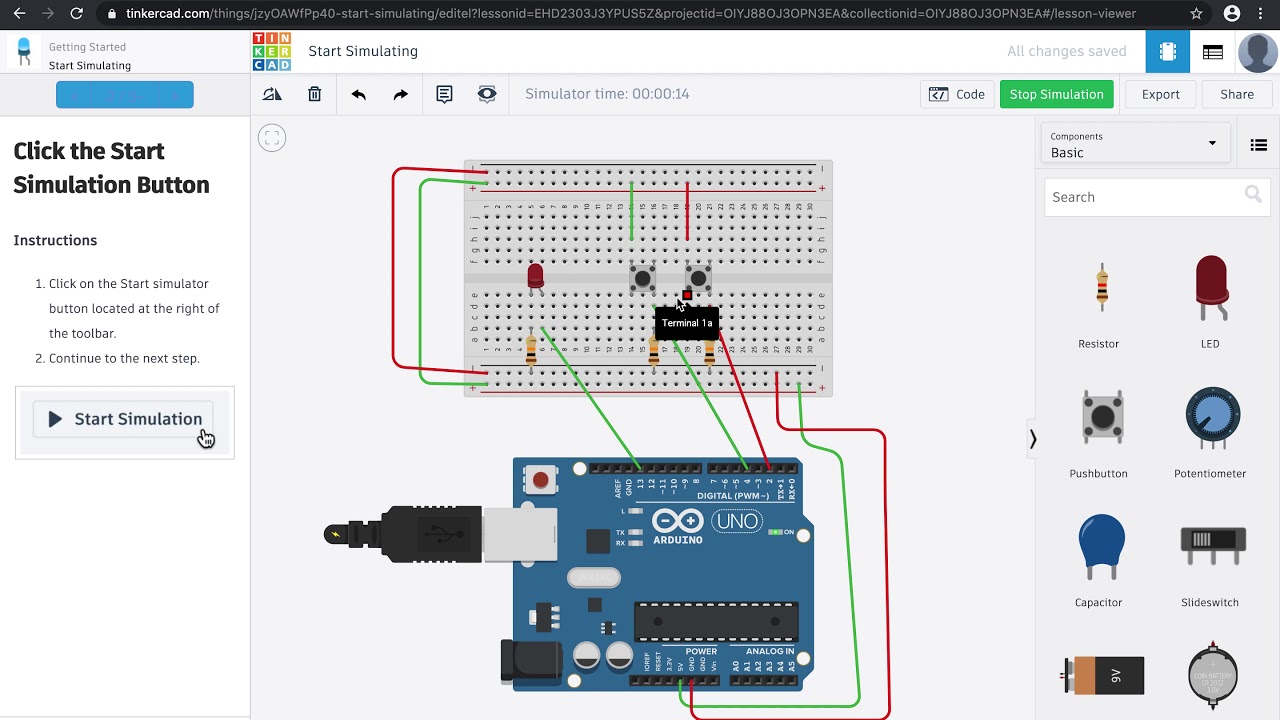
- #SIMULATE BLUETOOTH COMMUNICATIONS WITH ARDUINO SIMULATOR SERIAL#
- #SIMULATE BLUETOOTH COMMUNICATIONS WITH ARDUINO SIMULATOR CODE#
Since this library supports only master mode, this pin should be set always as OUTPUT otherwise the SPI interface could be put automatically into slave mode by hardware, rendering the library inoperative. Note about Slave Select (SS) pin on AVR based boardsĪll AVR based boards have an SS pin that is useful when they act as a slave controlled by an external master. Note that MISO, MOSI, and SCK are available in a consistent physical location on the ICSP header this is useful, for example, in designing a shield that works on every board.

The following table display on which pins the SPI lines are broken out on the different Arduino boards: With most SPI devices, after SPI.beginTransaction(), you will write the slave select pin LOW, call SPI.transfer() any number of times to transfer data, then write the SS pin HIGH, and finally call SPI.endTransaction().įor more on SPI, see Wikipedia's page on SPI. You should attempt to minimize the time between before you call SPI.endTransaction(), for best compatibility if your program is used together with other libraries which use SPI. Unless you, or some library, calls beginTransaction a second time, the setting are maintained. The SPI settings are applied at the begin of the transaction and SPI.endTransaction() doesn't change SPI settings. If other libraries use SPI from interrupts, they will be prevented from accessing SPI until you call SPI.endTransaction(). SPI.beginTransaction( SPISettings(14000000, MSBFIRST, SPI_MODE0)) The simplest and most efficient way to use SPISettings is directly inside SPI.beginTransaction(). The SPI port will be configured with your all of your settings. Once you have your SPI parameters, use SPI.beginTransaction() to begin using the SPI port. The four modes combine polarity and phase according to this table: These modes control whether data is shifted in and out on the rising or falling edge of the data clock signal (called the clock phase), and whether the clock is idle when high or low (called the clock polarity). Generally speaking, there are four modes of transmission. This means you have to pay special attention to the device's datasheet when writing your code. The SPI standard is loose and each device implements it a little differently.
#SIMULATE BLUETOOTH COMMUNICATIONS WITH ARDUINO SIMULATOR CODE#
To write code for a new SPI device you need to note a few things:
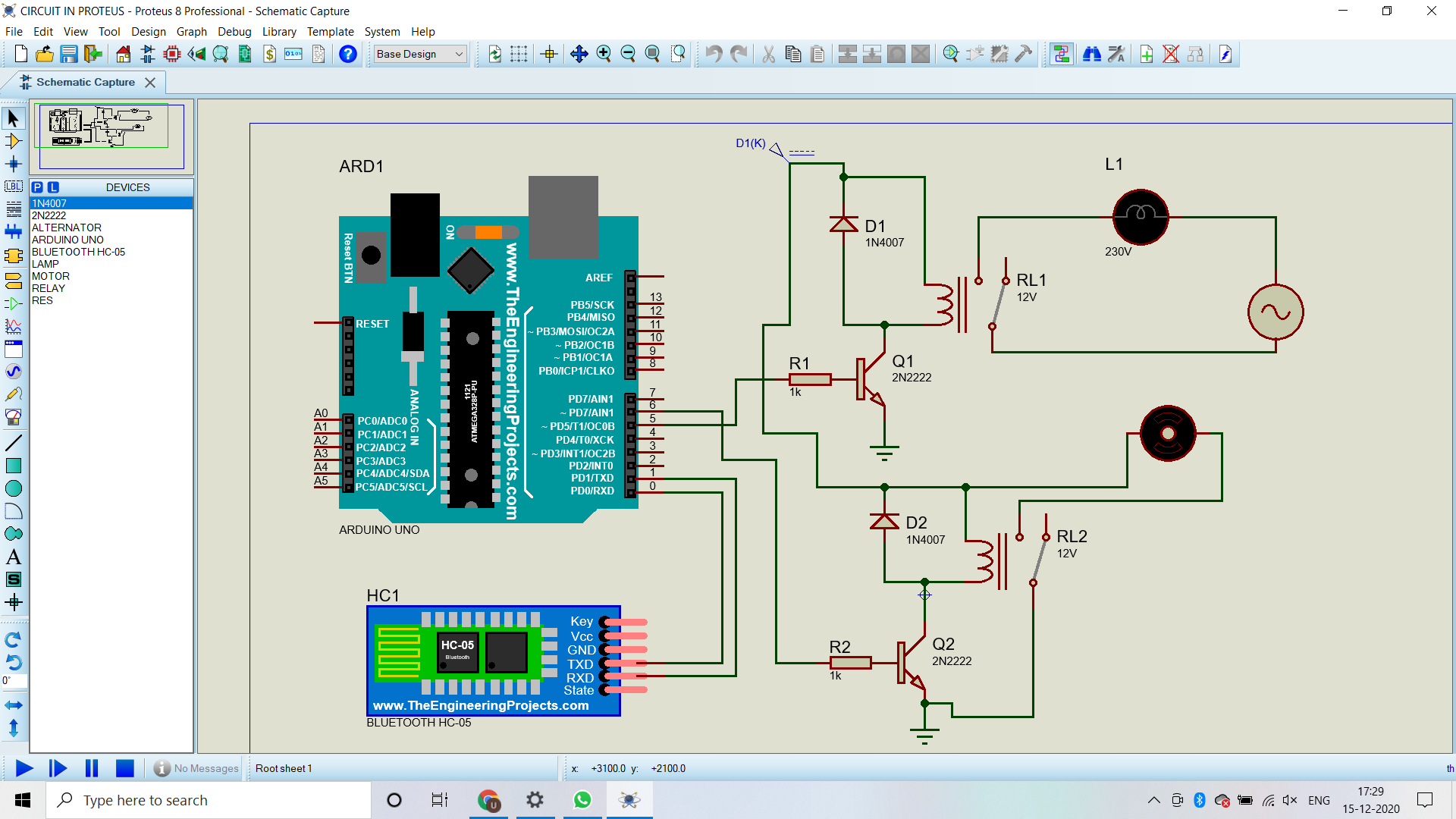
This allows you to have multiple SPI devices sharing the same MISO, MOSI, and CLK lines. When a device's Slave Select pin is low, it communicates with the master.
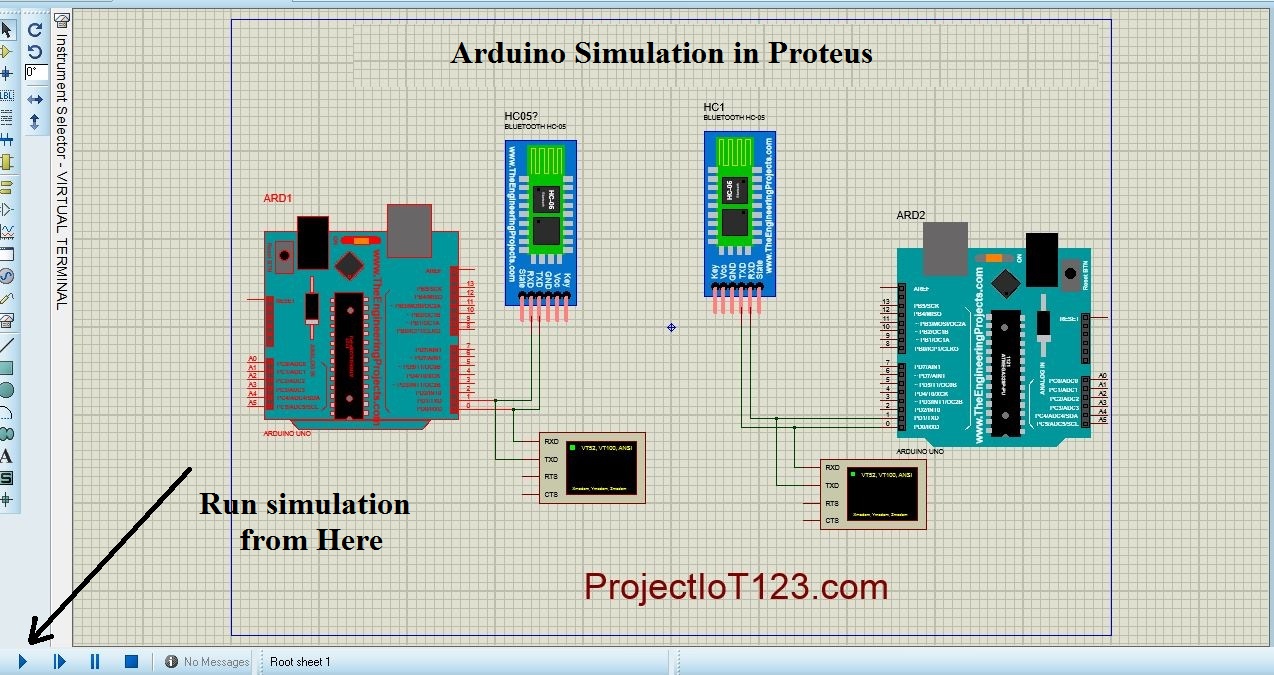
#SIMULATE BLUETOOTH COMMUNICATIONS WITH ARDUINO SIMULATOR SERIAL#
Serial Peripheral Interface (SPI) is a synchronous serial data protocol used by microcontrollers for communicating with one or more peripheral devices quickly over short distances. This library allows you to communicate with SPI devices, with the Arduino as the master device.Ī Brief Introduction to the Serial Peripheral Interface (SPI) Reference Language | Libraries | Comparison | Changes


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
